Page 473 - IRSEM_Main Book
P. 473
Para No. 19.11.7(d) Annexure: 19-A3
Method for Finding Out the Resistance of an Earth
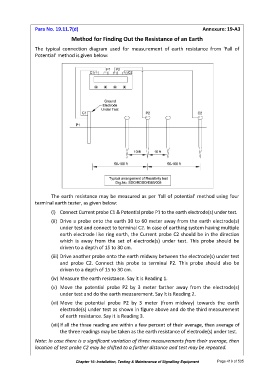
The typical connection diagram used for measurement of earth resistance from ‘Fall of
Potential’ method is given below:
The earth resistance may be measured as per ‘fall of potential’ method using four
terminal earth tester, as given below:
(i) Connect Current probe C1 & Potential probe P1 to the earth electrode(s) under test.
(ii) Drive a probe onto the earth 30 to 60 meter away from the earth electrode(s)
under test and connect to terminal C2. In case of earthing system having multiple
earth electrode like ring earth, the Current probe C2 should be in the direction
which is away from the set of electrode(s) under test. This probe should be
driven to a depth of 15 to 30 cm.
(iii) Drive another probe onto the earth midway between the electrode(s) under test
and probe C2. Connect this probe to terminal P2. This probe should also be
driven to a depth of 15 to 30 cm.
(iv) Measure the earth resistance. Say it is Reading 1.
(v) Move the potential probe P2 by 3 meter farther away from the electrode(s)
under test and do the earth measurement. Say it is Reading 2.
(vi) Move the potential probe P2 by 3 meter (from midway) towards the earth
electrode(s) under test as shown in figure above and do the third measurement
of earth resistance. Say it is Reading 3.
(vii) If all the three reading are within a few percent of their average, then average of
the three readings may be taken as the earth resistance of electrode(s) under test.
Note: In case there is a significant variation of three measurements from their average, then
location of test probe C2 may be shifted to a farther distance and test may be repeated.
Chapter 19: Installation, Testing & Maintenance of Signalling Equipment Page 419 of 535